Intelligent Robotics Control
본문
Overview
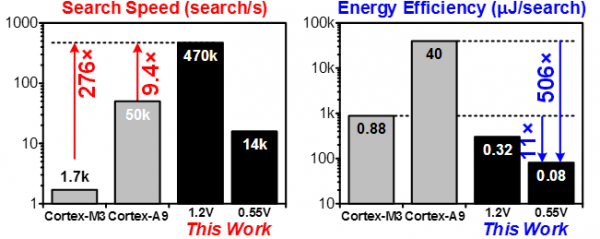
Micro robots with artificial intelligence (AI) are being investigated for many applications, such as unmanned delivery services. The robots, shown in Fig. 14.3.1, have enhanced controllers that realize AI functions, such as perception (information extraction) and cognition (decision making). Historically, controllers have been based on general-purpose CPUs, and only recently, a few perception SoCs [1-3] have been reported. SoCs with cognition capability have not been reported thus far, even though cognition is a key AI function in micro robots for decision making, especially autonomous drones. Path planning and obstacle avoidance require more than 10,000 searches within 50ms for a fast response, but a software implementation running on a Cortex-M3 takes ~5s to make decisions. Micro robots require 10× lower power and 100× faster decision making than conventional robots because of their fast movement in the environment, small form factor, and limited battery capacity. Therefore, an ultra-low-power high-performance artificial-intelligence processor (AIP) is necessary for micro robots to make fast and smart maneuvers in dynamic environments filled with obstacles. We present an ultra-low-power AIP consuming 1.1mW at 0.55V supply and 7MHz clock frequency for autonomous navigation of intelligent micro robots. In order to meet the target performance, 400,000search/s (~2× higher than 10,000 searches in 50ms), the proposed AIP has 3 key features: 1) an 8-thread treesearch processor (TSP) and a reinforcement learning accelerator (RLA) for real-time decision making, 2) a 3-level artificial intelligence cache (AI$) to reduce duplicated computations, and 3) an on-chip PVT monitoring and compensation circuit for stable and high-speed operation at near-threshold voltage (NTV).
Features
- 8-thread Tree Search Processor
- Reinforcement Learning Accelerator
- 3-level Artificial Intelligence Cache
- On-chip PVT Compensation Circuit
Related Papers
- ISSCC 2016 [pdf]