BONE-V3
본문
Overview
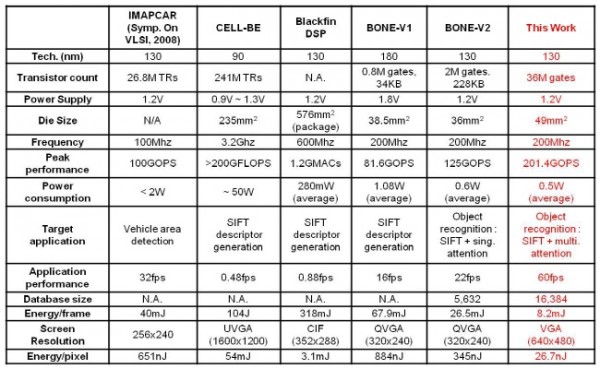
An attention controlled multi-core architecture is proposed for energy efficient object recognition. The proposed architecture employs two IP layers having different roles for energy efficient recognition processing: the attention/control IPs compute regions-of-interest (ROIs) of the entire image and control the multiple processing core stopper form local object recognition processing on selected area. To this end, a task manager is proposed to perform dynamic scheduling of various ROI tasks from the attention IP to multiple cores in a unit of small-sized grid-tile. Thanks to a number of grid-tile threads generated by the task manager, the utilization of the multiple cores amounts to 92% on average. As a result, the proposed architecture achieves2.1x energy reduction in multi-core recognition system by indicating processing cores to focus on critical area of the image with a 0.87mJ attention processing. Finally, the proposed architecture is implemented in 0.13 mm CMOS technology and the fabricated chip verifies 3.2xlower energy dissipation per frame than the state-of-the-art object recognition processor.


Attention controlled Multi-core architecture

Features
a. Three-stage task pipelined architecture
- Tile based region-of-interest (ROI) task magnitude
- MPipeline time balancing among three stages
b. Visual Perception Engine
- Neuro-fuzzy pixel classification for multi-object ROI detection
c. Multi-casting Network-on-Chip
- Combined topology + multi-casting capability
d. Workload-aware dynamic power management
- Adaptive power gating according to input workload