ANES
본문
Overview
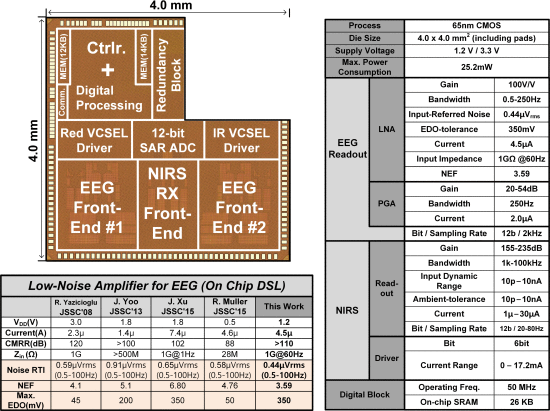
There has been recent research into continuous monitoring of the quantitative anesthesia (ANES) depth level for safe surgery [1]. However, the current ANES depth monitoring approach, bispectral index (BIS) [3], uses only EEG from the frontal lobe, and it shows critical limitations in the monitoring of ANES depth such as signal distortion due to electrocautery, EMG and dried gel, and false response to the special types of anesthetic drugs [3]. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is complementary to EEG [2], and can not only compensate for the distorted depth level, but also assess the effects of various anesthetic drugs. In spite of its importance, a unified ANES monitoring system using EEG/NIRS together has not been reported because NIRS signals have widely different dynamic ranges (10pA to 10nA), and also signal level variations from person to person and environment are not manageable without closed-loop control (CLC). In this paper, a multimodal head-patch system that simultaneously measures EEG and NIRS on the frontal lobe is proposed for accurate ANES depth monitoring. A 60dB dynamic range logarithmic TIA (logTIA) is adopted to amplify the photodiode (PD) signal and a CLC driver is used to compensate for the human-to-human variations. Also, an LNA with high Zin (1GΩ) and wide electrode DC-offset (EDO) cancelation range (350mV) is integrated to obtain reliable EEG signals.

Features
- Anesthesia Monitoring
- Headpatch System EEG+NIRS Monitoring
Related Papers
- ISSCC 2017 [pdf]